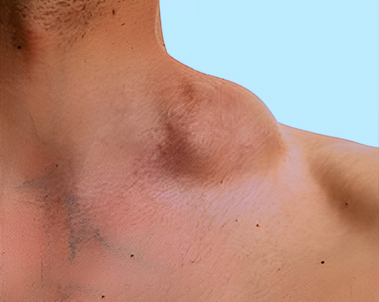
Lymphomas
Lymphoma is a cancer that begins in the immune system of the body i.e. a network of vessels and glands that help fight infection. There are two main types: Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Get In Touch

Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Each cell in the body contains DNA in its nucleus which controls its life cycle. For many reasons, this control mechanism stops working. Old cells do not die and instead grow out of control, forming new, abnormal cells, or a tumour.
Contact UsUsually, early cancer does not cause pain. The signs or symptoms will depend on where the cancer is, how big it is, and how much it affects the organs or tissues. But sometimes cancer starts in places where it won’t cause symptoms until it has grown quite large. Given below are certain general signs and symptoms to watch out for. There may be other causes for each of these, but it’s important to see a doctor about them as soon as possible especially if there’s no other cause you can identify, the problem lasts a long time, or it gets worse over time. Do not wait to feel pain.
Though it is very difficult to pinpoint any definite cause, certain substances, known as carcinogens, can definitely increase your chances of getting cancer.
Cancers are divided into different types based on where they originate

Lymphoma is a cancer that begins in the immune system of the body i.e. a network of vessels and glands that help fight infection. There are two main types: Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
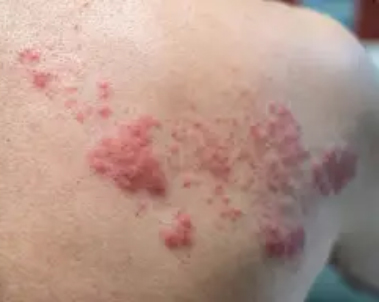
Multiple myeloma is cancer that begins in plasma cells, another type of immune cell. The abnormal plasma cells, called myeloma cells, build up in the bone marrow and form tumours in bones all through the body.
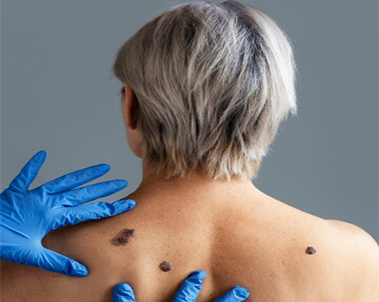
Melanoma is cancer that begins in cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. Most melanomas form on the skin, but melanomas can also form in other pigmented tissues, such as the eye.

A sarcoma begins in the tissues that support and connect the body like the fat, muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, blood or lymph vessels, cartilage or bone. Examples are osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma.
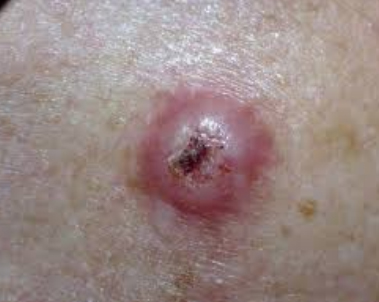
They are the most common types of cancers. A carcinoma begins in the skin or the tissue that covers the surface of internal organs and glands. Carcinomas usually form solid tumours. Examples of carcinomas include prostate cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer.
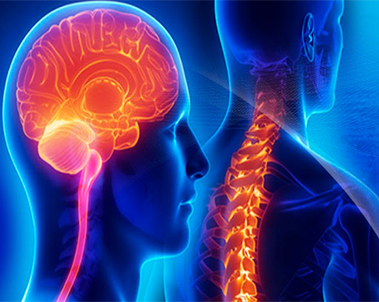
The central nervous system cancer tumours develop in the brain and spinal cord. These tumours are named based on the type of cell in which they formed and where the tumour first formed in the central nervous system.
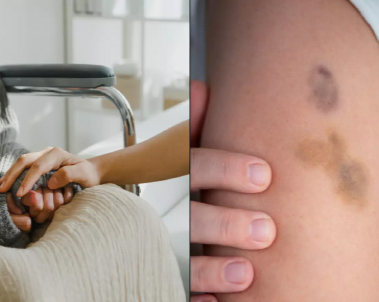
Cancers that begin in the blood-forming tissue of the bone marrow are called leukaemia. These cancers do not form solid tumours. A large numbers of abnormal white blood cells build up in the blood and bone marrow, crowding out normal blood cells. The four main types of leukaemia are acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL), chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), and chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML).